low normal lv systolic function | ejection fraction chart low normal lv systolic function Systolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction(HFrEF). Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage . See more SIA "ARTIVA" Katlakalna iela 1, Rīga, LV-1073, Latvija. Tel: +371 29252882; +371 29116116
[email protected]; www.enervent.lv.
0 · what causes low ejection fraction
1 · treatment for low ejection fraction
2 · systolic heart failure concept map
3 · reduced ejection fraction symptoms
4 · lv systolic function severely reduced
5 · end stage systolic heart failure
6 · ejection fraction chart
7 · ejection fraction 55 60
Our results of epicardial LV lead placement demonstrate a clear advantage of avoiding lead-related complications and the necessity of re-operations. Surgical LV lead placement offers the advantage of direct access to the lateral left ventricular wall.
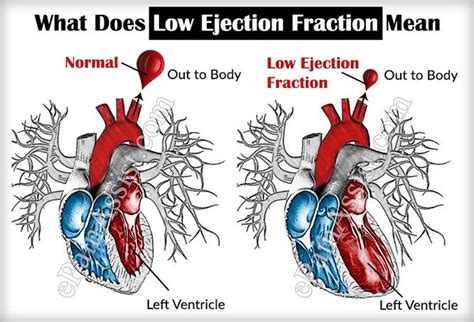
Systolic heart failure is a condition where the left ventricle of the heart can’t pump blood efficiently. It can be caused by various factors, such as coronary artery disease or hypertension, and can lead to fluid buildup and organ damage. Learn how to diagnose and treat this serious condition. See moreSystolic heart failure is a condition in which the left ventricle of your heart is weak. Your left ventricle is the largest and strongest chamber of your heart. It’s . See moreSystolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction(HFrEF). Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage . See moreAnyone can develop systolic heart failure, but it’s more common as people age. It typically occurs in people who have had another heart-related condition. See more
Ejection fraction (EF) is a percentage of blood pumped out by the left ventricle . Reduced left ventricular systolic function predicts worse outcomes. However, the . A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a . A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as .
Ejection fraction measures your heart’s ability to pump oxygen-rich blood out to your body. In a .Systolic heart failure is a type of heart failure that affects the left ventricle and reduces its ability to pump blood. Learn about the causes, symptoms, treatment and warning signs of systolic heart failure.
what causes low ejection fraction
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the .European Society of Cardiology and American Society of Echocardiography guidelines report normal LVEF as >50% and >55%, respectively (2, 3) and clinical HF trials have defined left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40-45% to . The clinical syndrome of heart failure (HF) can develop in patients with low, . Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. It’s a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood. The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF under 40% may indicate systolic heart failure.
A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure. Reduced left ventricular systolic function predicts worse outcomes. However, the optimal threshold for “normal” left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is uncertain. In general LVEF ≥ 55% is considered “normal” by guidelines, with a low normal designation for LVEF 50-55%.
A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a sign of heart failure or an underlying heart. A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Even if you have a normal ejection fraction, your overall heart function may not be healthy.Ejection fraction measures your heart’s ability to pump oxygen-rich blood out to your body. In a healthy heart, the fraction is a higher number. A low number means that your heart has difficulty keeping up with your body’s needs.
Systolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (or HFrEF). Ejection fraction is the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every beat. A normal, healthy ejection fraction is 55% to 65%. If it’s higher or lower, that can indicate a heart problem.Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .European Society of Cardiology and American Society of Echocardiography guidelines report normal LVEF as >50% and >55%, respectively (2, 3) and clinical HF trials have defined left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40-45% to indicate LV systolic dysfunction (4, 5).
The clinical syndrome of heart failure (HF) can develop in patients with low, mildly decreased, or normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement that represents the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every contraction. It’s a sign of how well your heart is pumping blood. The normal, healthy range for EF measurement is 55% to 70%. An EF under 40% may indicate systolic heart failure.
treatment for low ejection fraction
A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
Reduced left ventricular systolic function predicts worse outcomes. However, the optimal threshold for “normal” left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is uncertain. In general LVEF ≥ 55% is considered “normal” by guidelines, with a low normal designation for LVEF 50-55%.
A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a sign of heart failure or an underlying heart. A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Even if you have a normal ejection fraction, your overall heart function may not be healthy.Ejection fraction measures your heart’s ability to pump oxygen-rich blood out to your body. In a healthy heart, the fraction is a higher number. A low number means that your heart has difficulty keeping up with your body’s needs.Systolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (or HFrEF). Ejection fraction is the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every beat. A normal, healthy ejection fraction is 55% to 65%. If it’s higher or lower, that can indicate a heart problem.
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
European Society of Cardiology and American Society of Echocardiography guidelines report normal LVEF as >50% and >55%, respectively (2, 3) and clinical HF trials have defined left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40-45% to indicate LV systolic dysfunction (4, 5).

systolic heart failure concept map
reduced ejection fraction symptoms
Riga Technical University website. Studies, Science, Valorization, Internationalization, University, Faculties, Library, News, Events, Contacts
low normal lv systolic function|ejection fraction chart